A Comprehensive Guide to Automotive Suspension Systems: Functions, Types, and Applications
In modern automotive design and manufacturing, the automotive suspension parts play a crucial role. As one of the core components of a vehicle, the suspension system is not only critical for vehicle stability but also directly impacts ride comfort and handling performance. Despite its significant role in automobiles, many people remain unfamiliar with its workings and the various types of suspension systems. This article will delve into the fundamental concepts of suspension systems, explore different types, discuss their advantages and disadvantages, and consider practical applications to provide a thorough understanding of this complex yet vital technology.
I. Basic Functions of the Suspension System
The suspension system, composed of various automotive suspension parts, primarily serves several key functions:
Absorbing Impacts: The suspension system effectively absorbs vibrations and shocks from uneven road surfaces, preventing these impacts from directly affecting the vehicle’s body, thus enhancing driving comfort.
Maintaining Vehicle Stability: By controlling the movement of the wheels, the suspension system ensures that the wheels maintain good contact with the road, thereby improving vehicle handling stability and safety.
Optimizing Handling Performance: The design of the suspension system aims to optimize vehicle handling performance, ensuring that the vehicle remains stable under various driving conditions and performs well during turns or high-speed driving.
Enhancing Ride Comfort: By reducing body vibrations and sway, the suspension system significantly improves the comfort of passengers inside the vehicle.
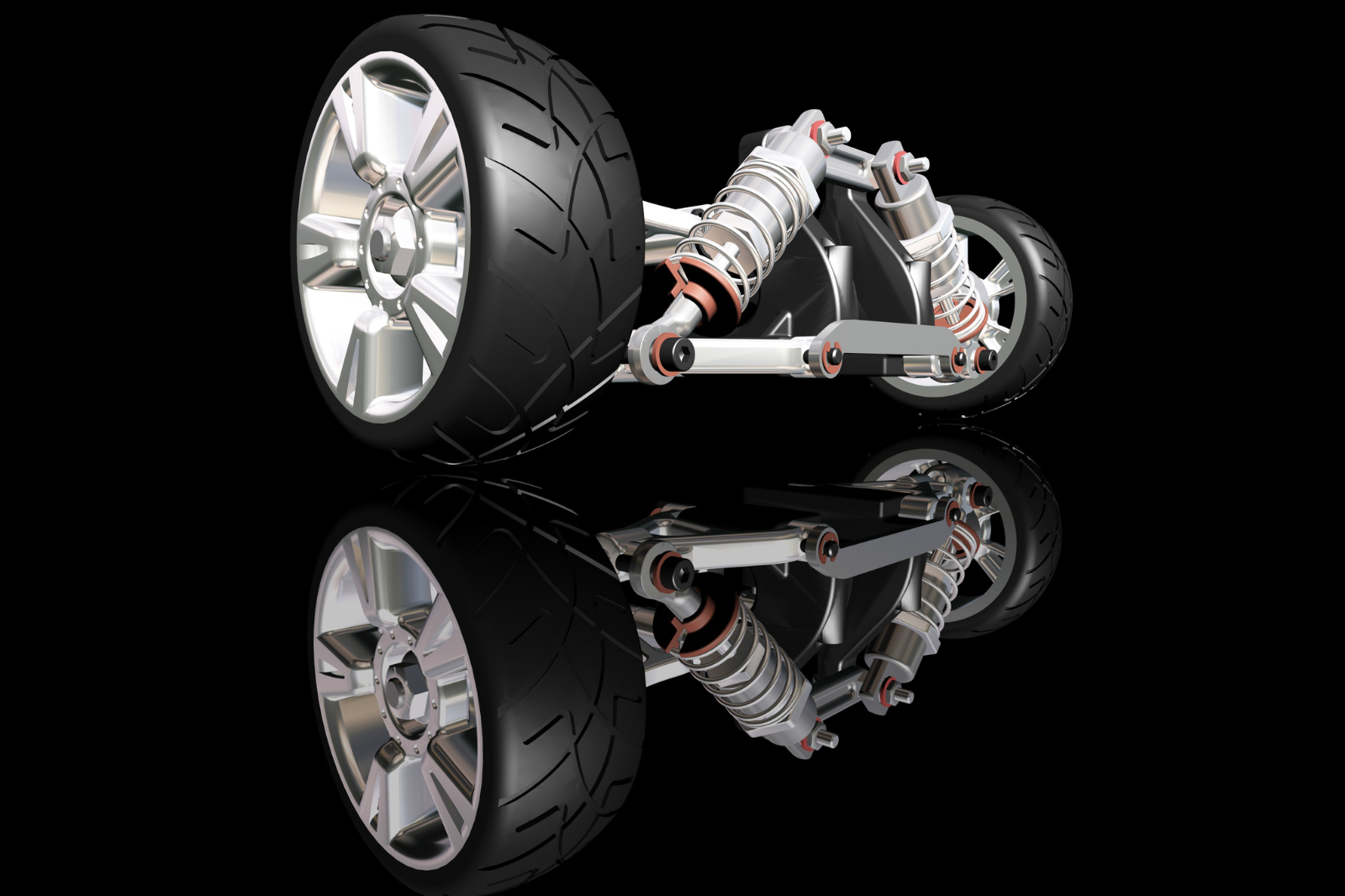
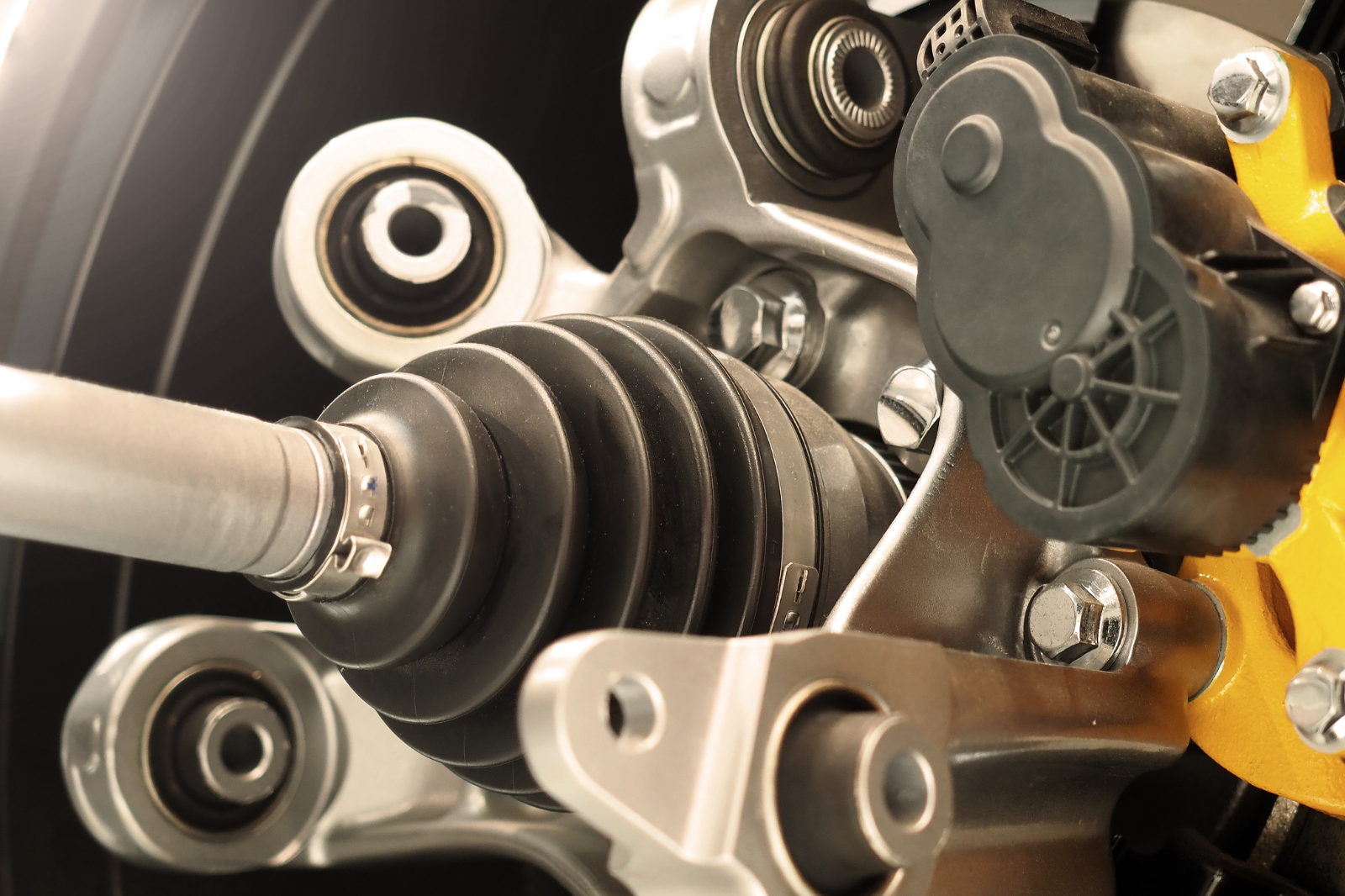
II. Main Components of the Suspension System
The suspension system primarily consists of three components, each crucial to the overall functionality of automotive suspension parts:
Elastic Elements:
- Coil Springs: Widely used in passenger cars to absorb road impacts effectively.
- Leaf Springs: Mainly used in commercial vehicles such as trucks and vans for high load-bearing capacity.
- Torsion Bars: Utilize torsional force to absorb shocks, commonly used in sports cars.
- Air Springs: Adjust the spring stiffness by altering air pressure, providing better comfort and handling.
Shock Absorbers:
- Hydraulic Shock Absorbers: Use liquid to provide damping, reducing body sway.
- Gas Shock Absorbers: Incorporate gas in addition to liquid to enhance damping performance.
Control Elements:
- Linkages and Arms: Include various types like multi-link, five-link, double wishbone, and MacPherson strut. These automotive suspension parts control the wheel’s movement trajectory.
- Upper and Lower Control Arms: Maintain the correct position and angle of the wheels, ensuring stability during vehicle motion.
III. Types of Suspension Systems
Suspension systems, including various automotive suspension parts, can be classified into independent and non-independent types, each with its unique design and application scenarios.
1. Independent Suspension Systems
Independent suspension systems allow each wheel of the vehicle to move independently, without affecting the other wheels. This design significantly improves the vehicle’s adaptability to uneven surfaces and enhances ride comfort. Common types include:
MacPherson Strut Suspension:
- Characteristics: Simple structure consisting of coil springs, shock absorbers, and a triangular lower control arm.
- Advantages: Low cost, easy maintenance, suitable for small cars and vehicles with large engines.
- Disadvantages: Limited lateral support, leading to greater body roll during cornering; usually not used in high-end models.
Double Wishbone Suspension:
- Characteristics: Composed of two V-shaped control arms, resulting in a more complex structure.
- Advantages: Greater lateral stiffness, excellent anti-roll performance, better grip, and clear road feedback. Suitable for high-performance and sports cars.
- Disadvantages: Larger space requirement, higher manufacturing and tuning costs, generally not used in small vehicles.
Multi-Link Suspension:
- Characteristics: Comprises three or more linkages, often found in rear suspensions with 4 or 5 links.
- Advantages: Provides excellent comfort and handling, each linkage works independently, enhancing flexibility and comfort.
- Disadvantages: High cost, large space requirement, rarely used in front suspensions.
2. Non-Independent Suspension Systems
In non-independent suspension systems, the wheels are connected by a rigid linkage, causing the movement of one wheel to affect the other. This design typically has lower manufacturing costs but offers less comfort and handling performance. Common types include:
- Torsion Beam Suspension:
- Characteristics: A single beam connects the two wheels, simple in structure and cost-effective.
- Advantages: Low manufacturing cost, durable structure, effective in reducing vertical body movement.
- Disadvantages: Limited ability to handle independent wheel movement, leading to stability issues when one wheel encounters a bump.
IV. Suspension System Selection and Application
When choosing a suspension system, various factors must be considered, including the vehicle’s intended use, budget, handling requirements, and comfort needs. Here are some practical considerations:
Vehicle Use:
- Passenger Vehicles: For passenger vehicles, comfort is often a top priority. MacPherson strut and multi-link suspensions are commonly used to provide good comfort and handling.
- Commercial Vehicles: Trucks and vans typically require higher load-bearing capacity, so leaf springs and torsion beam suspensions are preferred for durability and load capacity.
- Sports Cars: Sports cars demand high handling performance and stability, making double wishbone and multi-link suspensions ideal for enhancing handling and driving pleasure.
Budget:
- High-End Models: High-end vehicles often feature complex suspension systems such as double wishbone and multi-link suspensions to deliver superior handling and comfort.
- Economy Models: Economy vehicles often use MacPherson struts and torsion beam suspensions to keep manufacturing costs down while meeting basic driving needs.
Handling Requirements:
- Performance Vehicles: For vehicles requiring high handling performance, double wishbone and multi-link suspensions provide better feedback and stability.
- Comfort-Oriented Vehicles: For comfort-focused vehicles, multi-link suspensions and air springs are ideal due to their superior shock absorption capabilities.
V. Suspension System Tuning and Optimization
The design and selection of a suspension system provide the foundation, but the actual driving experience is also influenced by suspension system tuning. Manufacturers typically perform detailed tuning and optimization based on the vehicle’s target market and positioning. These adjustments include:
Spring Stiffness and Shock Absorber Settings:
- Spring Stiffness: Adjusting the stiffness of the springs to achieve the desired balance between comfort and handling performance.
- Shock Absorber Settings: Tuning the damping characteristics of the shock absorbers to control body movement and vibrations for an optimized driving experience.
Suspension Geometry:
- Wheel Alignment: Adjusting parameters such as wheel camber and toe to improve handling stability and comfort.
- Suspension Travel: Optimizing the range of suspension travel to ensure stability and comfort across various road conditions.
Dynamic Control Systems:
- Electronic Suspension Control: Some high-end vehicles feature electronic suspension control systems that adjust suspension parameters in real-time to adapt to different driving conditions and road surfaces.
- Air Suspension Systems: Air suspension systems adjust the vehicle’s ride height based on load and driving needs, providing improved comfort and adaptability.
Conclusion
Understanding the suspension system’s fundamental principles and various types, including the automotive suspension parts, helps consumers make informed decisions when evaluating or purchasing a vehicle. While each suspension type has its theoretical advantages and disadvantages, the actual driving experience is often influenced by the manufacturer’s tuning and optimization efforts. By familiarizing oneself with suspension system knowledge, consumers can better assess, select, and maintain their vehicles, ultimately enjoying a more comfortable and satisfying driving experience.
Juye is a leading manufacturer of steering system components, renowned for innovation and quality. With over 20 years experience and certifications like ISO9000 and IATF16949, We offer efficient production, technical excellence, and eco-friendly practices. Our goal is to provide tailored solutions for Automobile steering and transmission, enhance user experience, and contribute to sustainable development. Contact us now!



Leave a Reply